Understanding Light Waves: Frequency, Wavelength, and Applications
Light is an essential aspect of our daily lives, enabling us to see and interact with the world around us. But what exactly is light and how does it work? Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, which is a type of energy that travels through the vacuum of space at a speed of approximately 299,792,458 meters per second. It is characterized by its frequency and wavelength, which determine the color and intensity of the light. In this article, we will explore the properties and applications of light waves in more detail.
Frequency and Wavelength
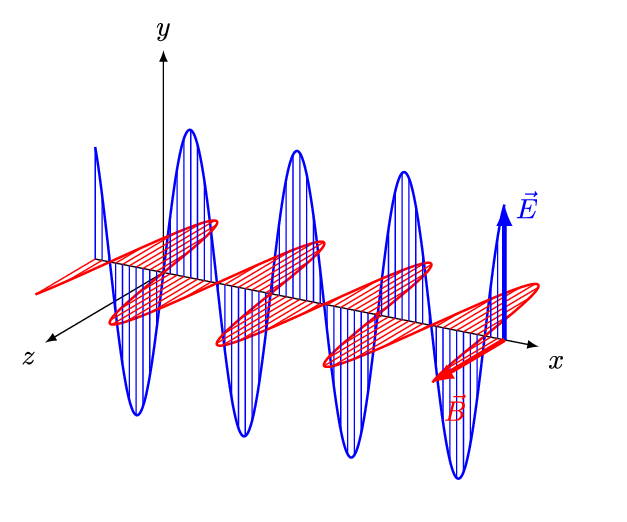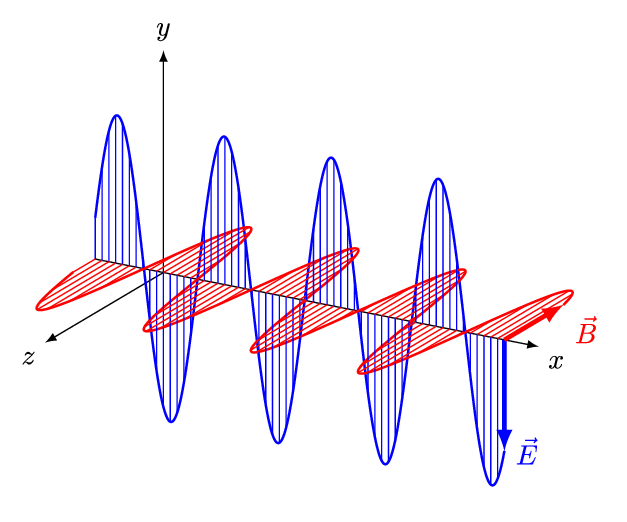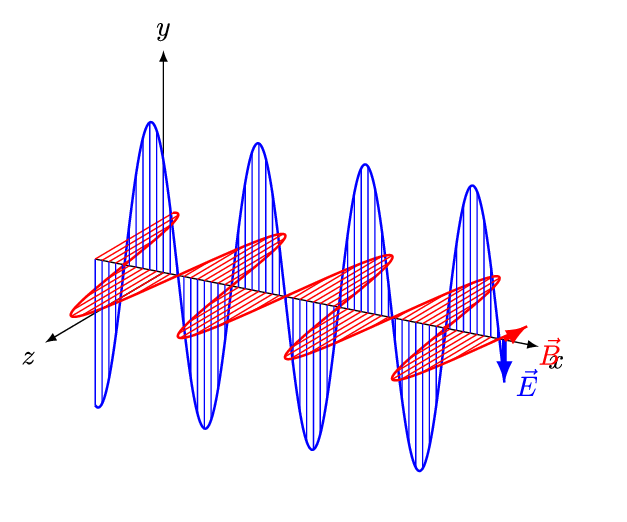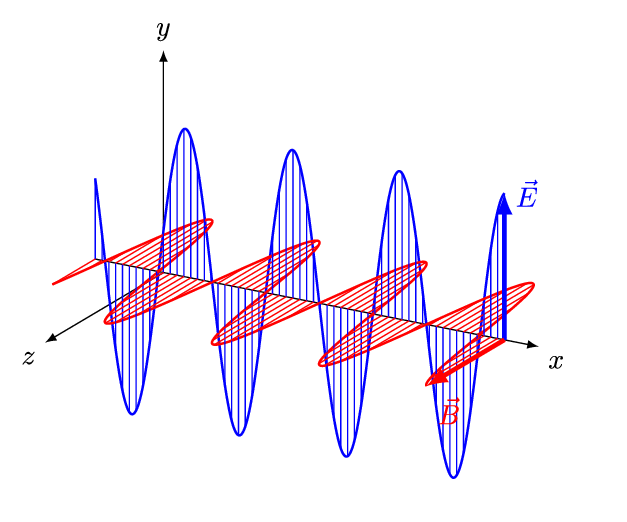
The frequency of a light wave is the number of times it oscillates or vibrates per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength and the more energy the light wave has. Conversely, the lower the frequency, the longer the wavelength and the less energy the light wave has. The different colors of light are caused by the different wavelengths of light waves. For example, red light has a longer wavelength than blue light, while violet light has a shorter wavelength than blue light.
The wavelength of a light wave is the distance between the peaks of consecutive waves, measured in meters. It is an important factor in determining the properties of a light wave, such as its energy and ability to interact with matter. For example, light waves with shorter wavelengths have more energy and are more likely to ionize atoms, while light waves with longer wavelengths have less energy and are less likely to ionize atoms.
Properties of Light Waves
Light waves have a number of properties that are important in various fields of study, such as physics, chemistry, and biology. Some of these properties include:
- Polarization: Light waves can be polarized, which means that the direction of the electric field is confined to a specific plane. Polarized light is often used in sunglasses and LCD screens to reduce glare and improve visibility.
- Reflection: Light waves can be reflected off of surfaces, such as mirrors and water. The angle at which the light is reflected is determined by the angle of incidence, which is the angle at which the light hits the surface.
- Refraction: Light waves can also be refracted, or bent, as they pass through different materials. This is what causes the apparent bending of light as it passes through water or glass.
- Absorption: Light waves can be absorbed by certain materials, which is what causes objects to appear a certain color. The color of an object is determined by the wavelengths of light that it absorbs and reflects.
- Scattering: Light waves can be scattered by particles in the air or in other materials, which is what causes phenomena such as the blue sky and red sunsets.
Applications of Light Waves
Light waves have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Communication: Light waves are used in various forms of communication, such as fiber optic cables and laser printers. Fiber optic cables use light to transmit information over long distances, while laser printers use light to transfer images onto paper. These technologies rely on the high speed and reliability of light waves to transmit data quickly and accurately.
- Medicine: Light waves are used in various medical procedures, such as laser surgery and phototherapy. Laser surgery uses focused light to cut or vaporize tissue, while phototherapy uses light to treat certain medical conditions, such as acne and seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
- Energy: Light waves can be converted into electricity through the use of solar panels, which are used to generate renewable energy. Solar panels use photovoltaic cells to absorb light and convert it into electricity, which can then be used to power homes and businesses.
- Astronomy: Light waves are also used in the study of astronomy, as they provide information about celestial objects and the universe. Astronomers use telescopes and other instruments to study the light emitted by stars, galaxies, and other objects in the sky.
Conclusion
In conclusion, light waves are a fundamental aspect of our world and have many important properties and applications. Understanding their frequency and wavelength allows us to understand the color and intensity of light, and to utilize light in various fields of study and technology. Whether it is through communication, medicine, energy, or astronomy, light waves play a crucial role in our daily lives and will continue to do so in the future.